How 555 timers Work - The Learning Circuit
Summary
TLDRIn this episode of 'The Learning Circuit,' Karen explores the 555 timer, a versatile and popular IC in hobby electronics. She delves into the internal workings of the 8-pin chip, detailing its components like comparators, flip-flop, and voltage divider. Karen explains the function of each pin and how they interact to create a timer, oscillator, or flip-flop. The video promises a future episode on practical applications of the 555 timer in various circuit modes.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The 555 timer is a widely used integrated circuit (IC) in hobby electronics, known for its versatility in various applications.
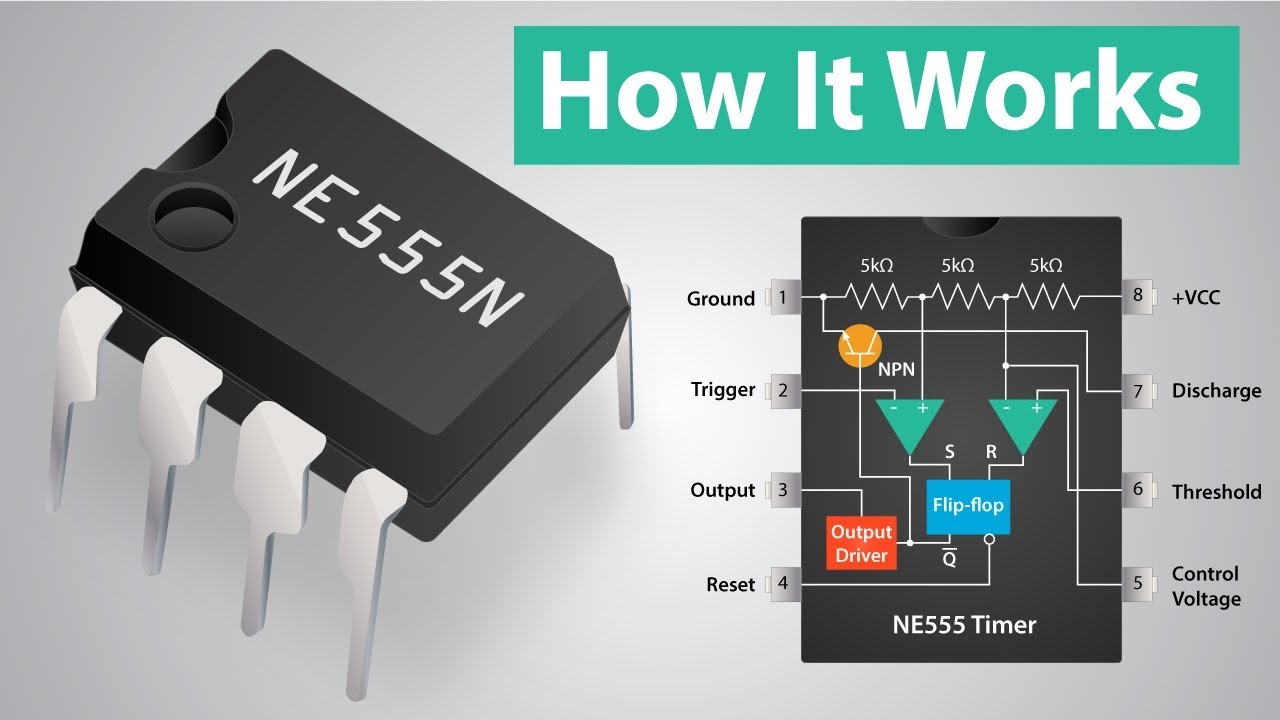
- 🔌 It features 8 pins, including ground (pin 1), trigger (pin 2), output (pin 3), reset (pin 4), control voltage (pin 5), threshold (pin 6), discharge (pin 7), and VCC (pin 8).
- 🏭 Inside the 555 timer, there are two comparators, a flip-flop, an inverter, two transistors, and a voltage divider made up of three 5kΩ resistors, which might be the origin of the '555' name.
- 🔋 The voltage divider divides the supply voltage (VCC) and feeds the comparators, with typical VCC values ranging from 5 to 15 volts.
- ⚖️ Comparators compare voltages at their inputs and output a digital signal indicating which input is larger, playing a crucial role in the 555's operation.
- 🔄 The flip-flop within the 555 timer is of the SR type, with set and reset inputs that control the output state, and only the NOT Q output is utilized.
- 🔧 The output of the flip-flop determines the state of the 555 timer's output pin, which is inverted before being outputted, creating a toggling effect.
- 🔩 Pin 5, the control voltage pin, can adjust the voltage at the negative input of comparator one, allowing for some control over the 555's operation.
- 🔄 Pin 4, when connected to VCC, ensures the 555 timer functions correctly; if grounded, it triggers a reset, causing the output to go low.
- 🔌 Pin 7, the discharge pin, is used with external capacitors to control the timer's duration, discharging the capacitor when the circuit is reset.
Q & A
What is the 555 timer and what is its primary function?
-The 555 timer is a widely used integrated circuit (IC) that functions as a timer, oscillator, or flip-flop. It is contained in an 8-pin IC and is popular in hobby circuits due to its versatility and ease of use.
How many pins does the 555 timer have and what are their typical functions?
-The 555 timer has 8 pins, which serve various functions: pin 1 is for ground, pin 2 is the trigger, pin 3 is the output, pin 4 is for reset, pin 5 is the control voltage, pin 6 is the threshold, pin 7 is the discharge, and pin 8 connects to VCC.
What are the main components inside the 555 timer?
-Inside the 555 timer, there are two comparators, a flip-flop, an inverter, two transistors, and a voltage divider made up of resistors.
How does the voltage divider inside the 555 timer work?
-The voltage divider is composed of three 56 kilo-ohm resistors and divides the supply voltage, feeding two comparators. It typically divides the VCC voltage so that one comparator receives two-thirds of the supply voltage and the other receives one-third.
What is the typical supply voltage range for the 555 timer?
-The typical supply voltage range for the 555 timer is from 4.5 to 16 volts, but VCC is usually between 5 and 15 volts.
How do the comparators in the 555 timer function?
-The comparators compare the voltages at their inputs and output a digital signal indicating which input is larger. If the positive input is larger, the output is high; if the negative input is larger, the output is low.
How does the flip-flop within the 555 timer contribute to its timing function?
-The flip-flop in the 555 timer has set and reset inputs that control its output. The flip-flop's output is used to control the timing function by setting and resetting based on the comparator outputs.
What is the purpose of the discharge pin (pin 7) on the 555 timer?
-Pin 7, the discharge pin, is used with external capacitors to control the timing duration of the timer. It connects to a transistor whose base is controlled by the flip-flop output, allowing the capacitor to discharge quickly when the circuit is reset.
How can the control voltage pin (pin 5) be used to modify the 555 timer's behavior?
-Pin 5, the control voltage pin, can be used to adjust the voltage at the negative input of comparator one, which typically receives two-thirds of VCC. This pin can be used to modify the timing behavior of the timer in certain applications.
What happens when both comparators in the 555 timer output high?
-When both comparators output high simultaneously, it is considered an invalid state because it causes the flip-flop's outputs to behave unpredictably. This situation should be avoided in proper circuit design.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
How Integrated Circuits Work - The Learning Circuit

Práctica 9: Circuito integrado 555

How to Make a Digital Stopwatch | DLD Project | Engineering 7.0 |
How a 555 Timer IC Works

Introduction to 555 Timer: The Internal Block Diagram and the Pin Diagram Explained

Como Fazer um Sequencial de Leds (muito simples)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)